Explanation of the new labor code: After implementing our new labor code last November 2025, the government has now published draft rules inviting public feedback within the prescribed deadlines of February 14, 2026 and January 30, 2026 for the industrial relations rules. These draft rules are important as they outline several key provisions that include salary definition for gratuity, overtime payment norms, rest days, contract labor conditions, grievance redressal mechanism, compliance obligations for firms, requirement of appointment letter, employee benefits, standing orders in all sectors and creation of worker re-skilling fund. According to EY, in response to the regulations, organizations should conduct a comprehensive review of HR, finance, payroll and legal functions, supported by impact assessments and policy revisions, to align with the new labor law framework.
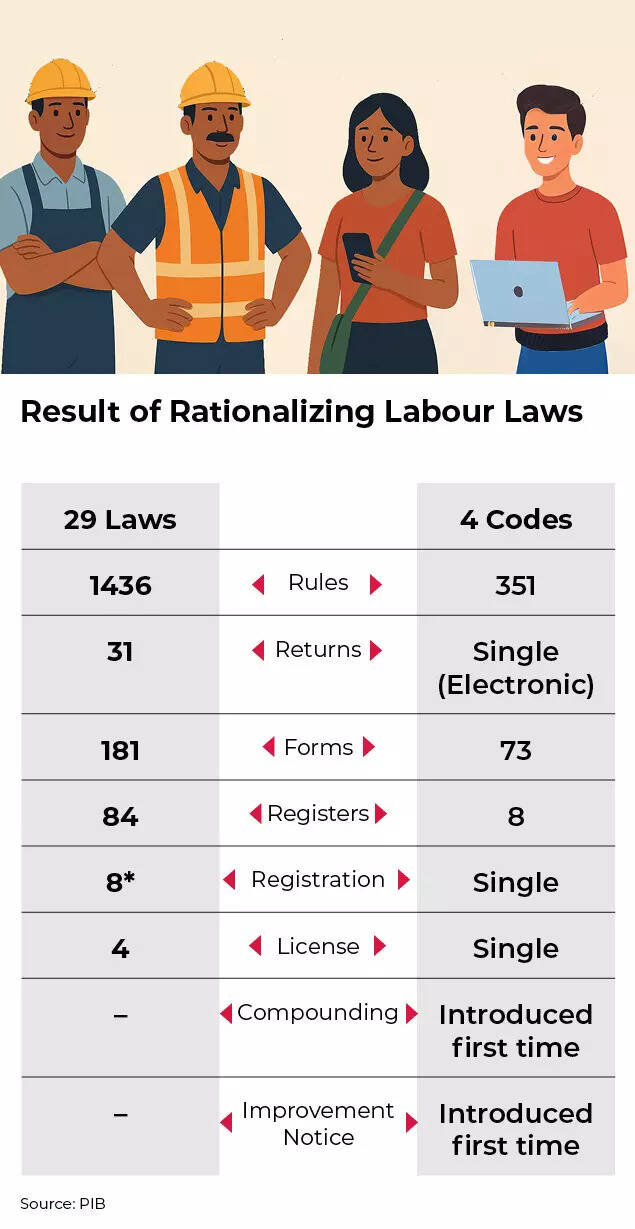
Result of rationalization of labor laws
New labor codes: What do the draft rules clarify?
The biggest clarification from the release of the draft rules is on the definition of wages. Salary calculation is important as it is what decides the gratuity amount individuals receive when they leave their jobs.According to the draft rules, the salary includes:All remuneration whether in the form of salary, allowances or otherwise payable to an employed person. This includes: Basic Pay, Dearness Allowance, Retaining Allowance, if any If the payments/allowances other than basic pay, dearness allowance and retaining allowance exceed the notified 50% or such percentage of all remuneration, the amount exceeding 50% or such notified percentage shall be added to ‘wages’.What is the 50% rule for allowances?If allowances and benefits together (except gratuity and retrenchment compensation) exceed 50% of all remuneration, the excess amount will be added back to the salary. This additional amount will be treated as wages for statutory purposes. Leave encashment is not a part of allowance.Let us understand the allowance rule with the help of an example:
- Total Remuneration: Rs 76,000 per month
- Basic Salary + Dearness Allowance: Rs 20,000
- Allowances: Rs 40,000
- Other components (gratuity and retrenchment compensation): Rs 16,000
- Total Pay Allowance: Rs 56,000
- The maximum allowance allowed for calculation of salary (50% of total remuneration) will be Rs 38,000
- Additional allowance above 50% limit is Rs 2000. This Rs 2000 will be added back to the salary (Basic Pay + DA) for statutory compliance.
- Statutory calculation will be done on revised salary: Rs 22,000
As per the Social Security Code, 2020, gratuity is to be calculated on the basis of the rate of “wages” last drawn by the employee. The rules clarify that for the purpose of determining gratuity, the exclusion from ‘salary’ will include any payment payable on an annual basis, which is linked to the performance or productivity of an employee or the establishment in which he is employed and does not form part of the remuneration payable under the terms of employment.

FAQs on New Labor Codes
Additionally, the following will not form part of ‘wages’ –
- Reimbursement of medical expenses;
- the cash equivalent of stock option benefits or stock awards;
- crèche allowance;
- Telephone and Internet reimbursement; And
- Value of meal voucher.
However, according to EY analysis, the rules have not yet clarified whether such components will be covered within the 50% limit on exclusion in the definition of ‘wages’. When is gratuity payable?Gratuity will be payable in the following events:
- upon termination
- On retirement (retirement due to age)
- on resignation
- In case of death or disability due to accident or illness
- On expiry of a fixed term employment contract
- On any other event notified by the Central Government
How is gratuity calculated?The calculation is simple: For each completed year of service or part thereof in excess of six months: 15 days’ wages per year based on the rate of wages last drawn (or such number as notified by the Central Government). The maximum gratuity notified by the Central Government is currently Rs 20 lakh.weekly holidays or rest daysEmployees will be entitled to at least one ‘rest day’ per week. The employee shall not be required or permitted to work on a rest day unless he has a day of rest substituted for a full day on one of the working days in the week immediately preceding or following the rest day. The new rules stated that no substitution could be made that would result in the employee working for more than ten consecutive days without taking a full day’s rest.appointment letter rulesAppointment letters will have to be issued to all employees in an establishment within 3 months of the implementation of the new labor rules.Overtime Rules:If certain working hour criteria are met, employees will be entitled to overtime pay. As per Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions (OSHWC) regulations, if an employee works as a daily wage earner in an organization for more than 8 hours in any day or more than 48 hours in any week, they will be entitled to wages at double the rate of their wages for overtime and will be paid at the end of each wage period. Accordingly, ‘Employees’ will be entitled to overtime for work exceeding 48 hours in a week (without any limit on daily working hours for the applicability of overtime). Labor Code: New Benefits RulesWomen working after 7 pm: There are rules for employment of women in night shifts (i.e., after 7 pm and before 6 am) – written consent of women employees is required and pick and drop transportation facility is mandatory. Medical Medical Examination: Every employer of a factory, dock, mine, building and other construction work shall ensure annual free medical examination for every employee. For people who have completed 40 years of age, this should be within 120 days of the start of the calendar year. An employer can avail the facility of medical examination of the employee under the relevant rule of Social Security Code Rules, 2025 through the Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC). Crèche Allowance: The employer and the negotiating union/council or the majority of the employees of the establishment (in the absence of the negotiating union/council) may enter into an agreement for the provision of crèche facility in the establishment and if not provided, for wage crèche allowance, which shall not be less than Rs. 500 per month per child. Traveling Allowance to Interstate Migrant Workers: Employers are required to pay traveling allowance to interstate migrant workers once in 12 months for commuting from the place of employment to the place of residence. Labor Re-Skilling Fund Any employer who retrenches any employee shall, within 10 days of such retrenchment, transfer to the account maintained by the prescribed Labor Commissioner, an amount equal to 15 days of the last drawn salary of such worker(s).The amount received from the employer can be transferred electronically by the Labor Commissioner to the account of the retrenched worker within 45 days of retrenchment, so that the employee can use the amount for re-skilling. appointment of contract workers Subject to exceptions, employment of contract labor in the core activities of an establishment is not permitted. As per OSHWC rules, the Joint Secretary, Ministry of Labor and Employment (‘MoLE’) to the Government of India is empowered to pass orders on the question whether an activity is classified as a main activity or not. Other conditions regarding appointment of contract labor include:
- If the contractor fails to do so then the principal employer will have to pay minimum bonus to the contracted workers.
- The principal employer has to pay to the contractor the amount due in respect of the salaries of the employees. The condition of making such payment before the date of payment of wages to contractual workers, as proposed in the earlier draft Central Rules issued on 7 July 2020, has been removed.
- Workers regularly employed by the contractor will be given annual increment of at least 2% of the salary (they will be excluded from the “contract labour” definition).
- Where a contractor wishes to obtain CLRA license for more than one State/All India, a common license can be applied for on the Shram Suvidha Portal or the designated portal of MOLE.
- Experience certificates will be issued to contract workers on demand, giving details of period, work done and experience gained in various fields.
compliance requirements
- In case of death/whereabouts of an employee is not known, nomination in specific format will have to be obtained from the employees for payment of due amount.
- Integrated annual return is to be filed every year.
- Establishments must maintain an employee register; Attendance Register-cum-Muster Roll; Register of wages, overtime, advances, fines and deductions; Register of women employees.
- The registers and records should be preserved in the original format for a period of 5 calendar years and should be maintained in English and Hindi or a language understood by the majority of persons employed.
Grievance Redressal RulesEvery industrial establishment which employs 20 or more workers must constitute a Grievance Redressal Committee which will look into resolving disputes arising out of individual grievances. The OSHWC rules introduce a provision to set up a separate grievance redressal mechanism for contract workers for redressal of grievances related to health, working conditions and wages. Complaints can be submitted at the level of the principal employer. Further, every establishment employing 500 or more workers shall constitute a Safety Committee in the prescribed manner and consisting of equal number of members representing the employer and workers, not exceeding 20. What the new rules mean for organisations: According to EY analysis, while the rules pre-published by the government under the Labor Code have introduced some significant changes to promote ease of doing business and simplify compliance, it is necessary for organizations to fully assess the implications of these changes. It recommends the following points for organizations to consider:
- Financial impact due to gratuity and leave encashment: Assess the additional cost to organizations on account of increased gratuity and leave encashment payments based on the new definition of ‘wages’ and the provisions of the Labor Code.
- Cost implications for other benefits under the rules: Evaluate the financial impact of overtime after 48 hours of work in a week, on-site crèche facility versus payment of crèche allowance; payment of traveling allowance; Conducting annual medical examination.

way forward
- Check for engagement of contract workers: The principal employer must conduct audit to verify that the contractor conforms to the prescribed requirements; Budget for 2% annual increase and compliance with minimum wage; Prohibition on hiring of contract workers for core activities, subject to exceptions.
- Operational changes for women working after 7 pm: Operational changes such as transportation, security and facility access may be required to accommodate longer shifts and night shifts for women employees.
- SOP for grievance redressal of on-roll employees and contract workers: Organizations must establish clear standing operating procedures for handling grievances raised and ensure disposal of complaints within the stipulated time frame.
- Establish a strong compliance framework: implement strong internal controls, conduct periodic clinical reviews and ensure effective governance.



.jpg?w=3800&h=2000&w=150&resize=150,150&ssl=1)






